What Muscles do Rowing Machines Work
Ever wondered what makes rowing machines such a hot topic in the fitness world? Well, you’re in for a treat because today we’re going to unravel the mystery of “What muscles do rowing machines work? As a fitness enthusiast and certified trainer, I’ve seen firsthand the transformative power of rowing workouts. Whether you’re a beginner looking to start your fitness journey or a seasoned pro looking to shake things up, understanding the muscles at play can make all the difference.
Imagine a full-body workout that engages muscles you didn’t even know existed. That’s the magic of rowing machines. From your arms and shoulders to your core and legs, rowing is like a symphony of muscle activation. But here’s the real question-which muscles are firing during the different phases of the rowing stroke? How can you optimize your technique to get the most out of every pull and push? Join me as we explore the ins and outs of rowing mechanics, uncover the key players in this muscle-building orchestra, and set you on the path to rowing success.
Whether you’re looking to build strength, burn calories, or simply enjoy a low-impact cardio workout, understanding the muscles you’re targeting is the first step to achieving your fitness goals. So let’s buckle up, grab the oars, and discover the world of rowing machine muscles!
Contents
- Introduction
- What Muscles Does the Rowing Machine Work?
- 1. Catch
- 2. Drive
- 3. Finish
- 4. Recovery
- Factors Affecting Efficiency
- Technique and Form
- Resistance and Intensity
- Stroke Rate and Duration
- Individual Variability
- Rowing for Muscle Gain
- What Muscles do Rowing Machines Work when Training Standing Up
- 1. Standing Upright Row:
- 2. Standing Bicep Curl:
- 3. Standing Leg Press:
- 4. Standing Core Twist:
- 5. Standing Shoulder Press:
- 6. Standing Lateral Raise:
- Benefits of Standing Rowing Machine Exercises
- Benefits of Using a Rowing Machine as a Workout
- Who is training with Rowing Machines suitable for?
- Summary
Introduction
The goal of this article is to delve into the intricate details of rowing exercises, focusing on the muscles they target and the factors that contribute to the effectiveness of these workouts. We will unravel the mysteries behind which muscle groups are engaged during different phases of the rowing stroke and examine how elements such as technique, resistance level, stroke rate, and individual characteristics affect the overall effectiveness of rowing machine workouts. Our goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to optimize rowing exercises for maximum benefit.
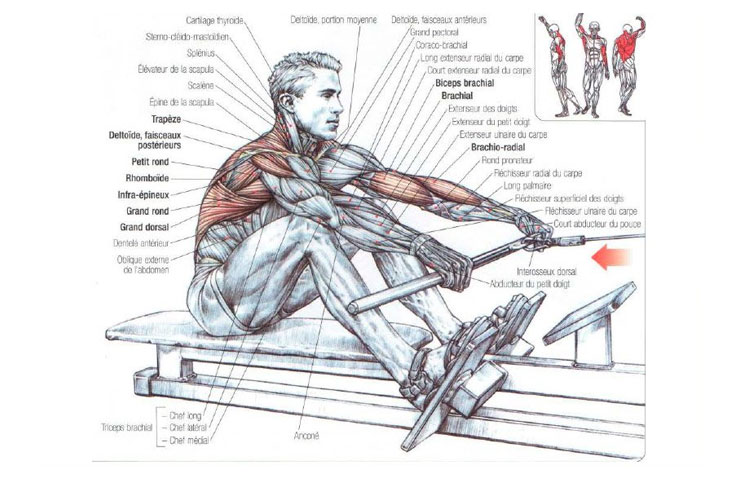
What Muscles Does the Rowing Machine Work?
Rowing exercises are a symphony of muscle engagement, orchestrating a harmonious interplay of several major muscle groups during different phases of the rowing motion. Let’s break down the key players in each phase:
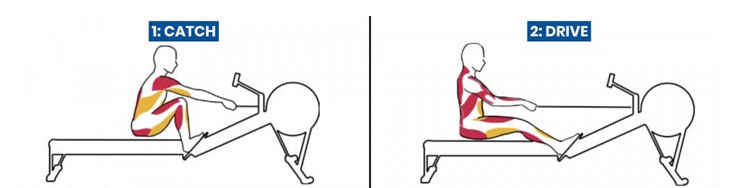
1. Catch
The catch phase is the starting point of the rowing stroke. Begin by sitting on the rower with your feet firmly planted on the footplates. Keep your knees slightly bent and your shins vertical. Your back should be straight and lean slightly forward from your hips, maintaining a neutral spine. Grasp bar with overhand grip, arms extended and shoulders relaxed.
As you initiate the stroke, drive through your heels while keeping your core engaged. Feel the contraction in your quadriceps as your legs straighten, while allowing your hip flexors to provide stability to your core. Maintain an upright posture throughout the movement, avoiding any rounding of the back.
2. Drive
Transitioning to the drive phase, continue to push through your heels, pushing against the footplate. As your legs straighten, engage your glutes and core muscles to transfer power from your lower body to your upper body. At the same time, initiate the pull by driving your elbows back, engaging your latissimus dorsi and trapezius muscles.
Imagine pulling the bar toward your lower ribs while keeping your back straight and strong. Your back angle should remain constant until your legs are fully extended. The power generated by your legs and the engagement of your back muscles create a powerful, explosive movement.
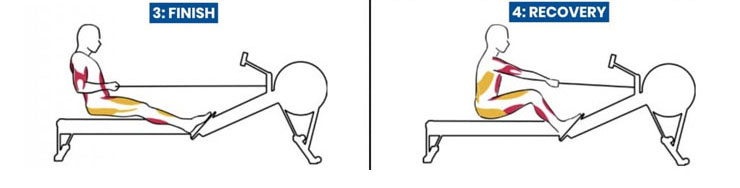
3. Finish
As you near the ed of the pull, begin the finish phase by leaning your torso back slightly, using your core to maintain balance. At this point, your legs are fully extended and your torso is slightly tilted back. To engage your posterior chain, focus on squeezing your glutes and hamstrings. At the same time, use your triceps and posterior deltoids to guide the bar toward your torso.
This engagement not only maximizes force output, but also helps you transition smoothly into the recovery phase. Maintain a strong, stable core to support your posture throughout the finishing phase.
4. Recovery
As you transition bck to the catch position for the next stroke, begin by allowing your arms to fully extend and then swing forward from your hips. Slide forward on the seat, allowing your knees to bend slightly and your shins to return to a vertical position. Keep your core engaged as you return to the starting position.
This phase is about controlled movement and muscle relaxation. Maintain proper posture and avoid slouching or rounding your back. Focus on a smooth transition from the finish to the catch, using your core and hamstrings to control the movement of the grip and seat.
Mastering the proper technique for each phase of the rowing stroke is key to optimizing your rowing machine workout. This not only maximizes muscle engagement, but also minimizes the risk of injury and ensures an efficient and effective full-body workout. As you practice these movements, pay attention to the coordination of muscle groups and the seamless transitions between phases, ultimately enhancing your rowing experience and fitness results.
Emphasizing the interconnectedness of muscle engagement and coordination during rowing is critical. It’s not just about isolated muscle groups; it’s about how they work together in perfect synchronization to create a seamless and powerful rowing stroke. The legs initiate power, the core stabilizes, the back muscles help generate power, and the arms and shoulders guide the movement, all while transitioning smoothly from one phase to the next. This harmonious interaction makes rowing an efficient and effective full-body workout.
Factors Affecting Efficiency
In order for training to be effective and safe, you steadily progress it is worth adhering to a number of principles, which we will describe below.
Technique and Form
Proper rowing technique plays a critical role in maximizing the efficiency of a rowing machine workout. When the technique is correct, it leads to optimal muscle engagement and injury prevention. Key points to consider include:
- Muscle Engagement: Proper rowing technique involves a coordinated movement between the legs, core, and upper body. Initiating the drive with leg power and following through with a controlled pull of the handle engages large muscle groups such as quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, back muscles, and core. A well-executed stroke ensures that these muscles are used efficiently, leading to a more effective workout.
- Injury Prevention: Incorrect rowing technique can lead to various injuries, especially to the lower back, shoulders, and wrists. Using improper form can strain these areas and increase the risk of injury. Learning and maintaining correct technique helps distribute the workload evenly across muscles and reduces the likelihood of overloading specific areas.
Resistance and Intensity
Adjusting resistance levels on a rowing machine impacts the muscle recruitment and overall effectiveness of the workout:
- Muscle Recruitment: Higher resistance levels simulate the feeling of rowing on water, requiring more force to complete each stroke. This engages a greater number of muscle fibers and increases the workload on muscles, contributing to strength and muscle development.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Lower resistance settings combined with a higher stroke rate can provide a more cardio-focused workout. This may improve endurance and cardiovascular fitness.
- Workout Effectiveness: The right balance of resistance and intensity can determine the effectiveness of the workout. Overloading with excessive resistance may lead to compromised technique or early fatigue, while too little resistance might not provide enough challenge for muscle development.
Stroke Rate and Duration
The stroke rate (strokes per minute) and workout duration are interconnected and impact muscle fatigue:
- Muscle Fatigue: Higher stroke rates can lead to quicker muscle fatigue, especially if combined with high resistance. Lower stroke rates might be more sustainable for longer durations, allowing for better endurance-focused training.
- Anaerobic vs. Aerobic Training: Higher stroke rates combined with shorter durations tend to emphasize anaerobic energy systems, which are beneficial for power and explosive strength. Lower stroke rates with longer durations lean more towards aerobic conditioning.
- Variation: Mixing up stroke rates and durations within your training regimen can help prevent plateaus and provide a well-rounded workout experience.
Individual Variability
Personal factors have a significant influence on rowing efficiency:
- Fitness Level: Individuals at different fitness levels will experience varying degrees of intensity and fatigue. Beginners might find lower resistance levels challenging, while advanced users require higher levels to maintain intensity.
- Body Composition: Body composition affects the distribution of muscle and fat, which can influence how efficiently you generate power and endure during workouts.
- Flexibility: Flexibility impacts the range of motion and fluidity of rowing strokes. Limited flexibility might hinder proper technique and reduce muscle engagement.
- Health Considerations: Pre-existing conditions or injuries can impact an individual’s ability to perform rowing exercises effectively. It’s important to adapt workouts based on health limitations.
In summary, the efficiency of rowing machine workouts is influenced by a combination of factors, including technique and form, resistance and intensity, stroke rate and duration, and individual variability. By understanding and optimizing these factors, individuals can tailor their rowing workouts to their goals and capabilities while maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks.
Rowing for Muscle Gain
When it comes to building muscle, rowing may not be the first exercise that comes to mind. However, rowing machines offer a unique and effective way to build muscle while providing a full-body workout. Whether you’re looking to add muscle mass, improve your overall strength, or diversify your workout routine, rowing can be a valuable tool in your fitness arsenal. Here’s what you need to know about using rowing to build muscle:
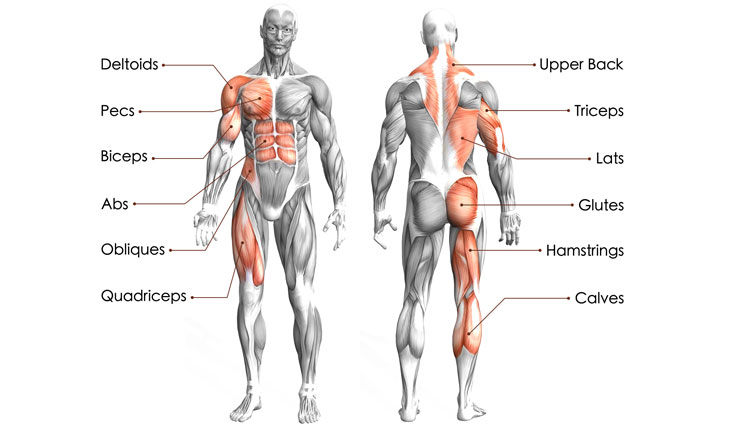
- Comprehensive muscle engagement: Rowing is a compound exercise that works multiple muscle groups simultaneously. The primary muscles worked during rowing include the legs (quadriceps, hamstrings), back (latissimus dorsi, rhomboids), core (abdominals, obliques), and arms (biceps, forearms). This holistic muscle activation provides a well-rounded approach to muscle development.
- Intensity and resistance: To stimulate muscle growth, it’s important to challenge your muscles with resistance. Rowers allow you to adjust the resistance level to simulate the sensation of rowing against water. Higher resistance settings require greater effort, which leads to muscle overload and ultimately contributes to muscle hypertrophy.
- Proper technique is important: As with any exercise, proper technique is critical for optimal muscle gain and injury prevention. Initiating the stroke with a strong leg drive and following through with controlled upper body movements ensures effective muscle engagement. Maintaining a neutral spine and avoiding excessive hunching or arching is essential to protect your back.
- Progressive overload: To see muscle gains over time, it’s important to use the principle of progressive overload. Gradually increase the resistance or duration of your rowing workouts to challenge your muscles. This encourages them to adapt and become stronger.
- Variation in Workouts: Variety in your rowing workouts can prevent plateaus and keep your muscles guessing. Experiment with different resistance levels, stroke rates, and workout durations. You can alternate between higher-intensity, shorter workouts and longer, endurance-oriented sessions to target different muscle fibers and energy systems.
- Nutrition and Recovery: Muscle growth requires proper nutrition and recovery. Eat a balanced diet that provides sufficient protein to support muscle repair and growth. Also, prioritize rest days to allow your muscles to recover and grow.
- Balance your cardiovascular training: While rowing is great for building muscle, it’s important to balance your cardiovascular training. Incorporating both strength-focused rowing sessions and cardio-focused rowing sessions can help you maintain your overall fitness while building muscle.
- Track your progress: Keep track of your workouts, including resistance levels, stroke rates, and duration. Tracking your progress can help you determine what works best for your muscle gain goals and make informed adjustments.
- Consistency is key: Consistency is key to building muscle. Make rowing a regular part of your routine and stay committed to your fitness goals.
What Muscles do Rowing Machines Work when Training Standing Up
Rowing machines are not limited to seated workouts; they also offer a range of standing exercises that target different muscle groups for a dynamic and engaging fitness experience. By incorporating standing exercises, you can diversify your routine and work different muscle groups while enjoying the benefits of a full-body workout. Here are some standing exercises you can perform on rowing machines and the muscles they target:
1. Standing Upright Row:
Muscles targeted: Shoulders (deltoids), upper back (trapezius, rhomboids), biceps.
How to Perform: Stand on footrests of rowing machine and grasp handle with overhand grip. Pull the handle toward your upper abdomen, leading with your elbows. This exercise engages your shoulder muscles and upper back, while involving your biceps as a secondary muscle.
2. Standing Bicep Curl:
Muscles targeted: Biceps.
How to Perform: Stand on footrest and grasp bar with underhand grip. Keeping your upper arms stationary, flex your elbows to bring the bar toward your shoulders. This isolates and targets your biceps muscles.
3. Standing Leg Press:
Muscles targeted: Quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes.
How to Perform: Stand on foot rests with feet shoulder width apart. Push against footrests to extend legs, simulating a leg press motion. This exercise effectively engages your lower body muscles and promotes leg strength and development.
4. Standing Core Twist:
Muscles targeted: Obliques, Core.
How to Perform: Stand on footrests and grasp bar with both hands in front of chest. Engage your core and twist your torso to one side, then the other. This exercise works your obliques and increases core stability.
5. Standing Shoulder Press:
Muscles targeted: Shoulders (deltoids), triceps.
How to Perform: Stand on footrest and grasp handhold at shoulder level. Raise bar, keeping arms fully extended. Return handhold to shoulder level. This exercise primarily targets your shoulder muscles, but also involves your triceps.
6. Standing Lateral Raise:
Muscles targeted: Shoulders (Deltoids).
Execution: Stand on foot rests and grasp handhold at sides. Raise bar sideways until it reaches shoulder height, then lower. This exercise isolates your shoulder muscles, helping to improve shoulder definition.
Benefits of Standing Rowing Machine Exercises
- Muscle diversification: Standing exercises engage different muscle groups than seated rowing, providing a well-rounded workout experience.
- Functional Strength: Many standing exercises mimic real-life movements, promoting functional strength and coordination.
- Core engagement: Standing exercises often require core stabilization, which improves core strength and balance.
- Dynamic workouts: Standing exercises add variety to your routine, keeping your workout fresh and motivating.
- Cardiovascular engagement: Standing exercises can increase your heart rate, contributing to cardiovascular fitness.
Standing exercises on rowing machines open up a world of possibilities for engaging different muscle groups and creating a more dynamic workout. By incorporating these exercises into your routine, you can develop well-rounded strength, improve balance, and diversify your fitness routine for optimal results.
Benefits of Using a Rowing Machine as a Workout
Rowing machine workouts offer a myriad of holistic benefits that contribute to overall health and well-being. This versatile exercise engages multiple muscle groups and provides a comprehensive workout experience, encompassing cardiovascular fitness, muscular strength and endurance, and the potential for weight loss.
- Cardiovascular Fitness: Rowing workouts are an exceptional way to enhance cardiovascular health. The rhythmic, full-body motion of rowing increases heart rate and stimulates blood circulation, effectively improving the efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Regular rowing can contribute to lowered resting heart rates, improved lung capacity, and enhanced overall endurance.
- Muscular Strength and Endurance: Rowing engages a wide array of muscles, including the legs, back, core, and arms. The push-pull motion against resistance helps to build both muscular strength and endurance. The leg drive initiates from the powerful muscles in the lower body, while the upper body contributes to the pulling phase, ensuring a comprehensive workout for major muscle groups.
- Full-Body Workout: One of the remarkable benefits of rowing is its ability to provide a full-body workout in a single exercise. As you glide back and forth on the rowing machine, you engage not only the larger muscle groups but also the stabilizing muscles that support posture and balance. This balanced engagement leads to a harmonious development of the entire body.
- Weight Loss and Calorie Burn: Rowing is an effective calorie-burning exercise, making it an excellent choice for those aiming for weight loss or weight management. The combination of cardiovascular conditioning and muscular engagement results in a high calorie expenditure during each session. Furthermore, rowing stimulates the afterburn effect, where the body continues to burn calories even after the workout is completed.
- Low-Impact Exercise: Unlike some other forms of cardiovascular exercise, rowing is low-impact, meaning it places minimal stress on the joints. This makes it a suitable option for individuals of various fitness levels, including those who might be recovering from injuries or looking for a joint-friendly workout.
- Improvement in Posture and Core Strength: Rowing encourages proper posture and core engagement throughout the entire motion. As you pull the handle towards you, your core muscles stabilize your spine and support the movement, which over time contributes to better posture and a stronger core.
- Versatility and Adaptability: Rowing machines offer a wide range of resistance levels, stroke rates, and workout durations, allowing you to tailor your workouts to your fitness goals. Whether you’re focusing on endurance, strength, or a combination of both, rowing can be adjusted to suit your preferences.
- Stress Reduction and Mental Clarity: Engaging in rowing workouts can have positive effects on mental health. The rhythmic and repetitive nature of rowing, combined with the release of endorphins during exercise, can help reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance mental clarity.
Incorporating rowing machine workouts into your fitness routine can lead to a well-rounded, effective approach to improving cardiovascular health, building muscle strength, and achieving weight management goals. Whether you’re an athlete seeking cross-training benefits or someone new to exercise, rowing offers a comprehensive and rewarding fitness experience.
An interesting piece by Stephanie Thielen on the benefits of training with the Rowing Machine with workout examples – at the link https://www.acefitness.org
Who is training with Rowing Machines suitable for?
Rowing machines can be suitable exercise options for many different types of people, here are some key considerations:
- All fitness levels – Rowing machines provide a full-body workout and can be adjusted for various resistance levels, making them adaptable for beginners to advanced exercisers. The smooth rowing motion is low-impact as well.
- Rehabilitation and injury recovery – The low-impact nature of rowing machines makes them a good option for rehabilitation from injuries or surgery, as well as for those with conditions like arthritis or joint pain that need a gentler workout. They allow the user to control the intensity.
- Seniors – Rowing is a beneficial exercise for seniors as it works major muscle groups, improves flexibility and cardiovascular health, and is low-impact. The seated position is stable and machines have adjustable resistance.
- Weight loss – Rowing machines burn calories and fat, making them effective for weight loss, especially vigorous rowing. Studies show rowing workouts can maximize calorie burn.
- Cross-training – Rowers and other athletes use rowing machines to complement their training. The full-body motion works muscles not hit as hard in their sport. It's a time-efficient cardio and strength workout.
- At-home workouts – Rowing machines are a popular home gym equipment choice as they provide an efficient, full-body cardio and strength workout in one compact machine. They require little space compared to other equipment.
So in summary, rowing machines can accommodate a wide range of fitness levels and goals, while providing an efficient, low-impact workout. Proper technique is important for getting the full benefit and avoiding injury. Consulting a fitness professional can help determine if a rowing machine matches your goals.
Summary
The key findings of the paper underscore the multiple benefits of rowing machine training for overall fitness. It emphasizes that rowing exercises offer a comprehensive approach to health, targeting cardiovascular fitness, muscular strength and endurance, and the potential for weight loss. The versatility of rowing machines allows individuals to tailor their workouts to specific goals and fitness levels, making them a valuable addition to any fitness program.
Understanding muscle engagement and efficiency emerges as a critical issue in optimizing the benefits of rowing exercise. Proper technique and form play a key role in ensuring optimal muscle recruitment while preventing the risk of injury. By initiating the stroke with the legs and transitioning through the core and upper body, users can effectively engage key muscle groups such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, back muscles and core. This balanced engagement not only maximizes the effectiveness of the workout, but also promotes a well-rounded development of muscular strength and endurance.
Understanding the relationship between resistance levels, cadence, and workout duration is paramount. Adjusting resistance levels influences muscle recruitment and cardiovascular intensity, tailoring the workout to emphasize either strength or endurance. In addition, varying stroke rates and durations within a workout prevents plateaus and ensures a comprehensive approach to fitness.
The importance of individual variability cannot be overstated. Fitness level, body composition, flexibility and health considerations all affect rowing efficiency. Adapting workouts to personal factors ensures a safe and effective exercise experience.
In conclusion, this paper highlights the holistic benefits of rowing machine training for cardiovascular health, muscular development, and weight management. It emphasizes the importance of proper technique, balanced muscle engagement, and understanding the interplay between resistance, stroke rate, and duration. By recognizing an individual’s unique characteristics, rowing enthusiasts can tailor their approach to maximize benefits and achieve a well-rounded, efficient workout routine.
Hopefully we’ve answered the question “What Muscles do Rowing Machines Work?” in detail, but if you still have questions, post them below in the comments.